# Laptop Coffee Lake Plus and Comet Lake
| Support | Version |
|---|---|
| Supported OpenCore version | 0.6.5 |
| Initial macOS Support(CFL) | macOS 10.13, High Sierra |
| Initial macOS Support(CML) | macOS 10.15, Catalina |
# Starting Point
So making a config.plist may seem hard, it's not. It just takes some time but this guide will tell you how to configure everything, you won't be left in the cold. This also means if you have issues, review your config settings to make sure they're correct. Main things to note with OpenCore:
- All properties must be defined, there are no default OpenCore will fall back on so do not delete sections unless told explicitly so. If the guide doesn't mention the option, leave it at default.
- The Sample.plist cannot be used As-Is, you must configure it to your system
- DO NOT USE CONFIGURATORS, these rarely respect OpenCore's configuration and even some like Mackie's will add Clover properties and corrupt plists!
Now with all that, a quick reminder of the tools we need
- ProperTree
- Universal plist editor
- GenSMBIOS
- For generating our SMBIOS data
- Sample/config.plist
- See previous section on how to obtain: config.plist Setup
And read this guide more than once before setting up OpenCore and make sure you have it set up correctly. Do note that images will not always be the most up-to-date so please read the text below them, if nothing's mentioned then leave as default.
# ACPI
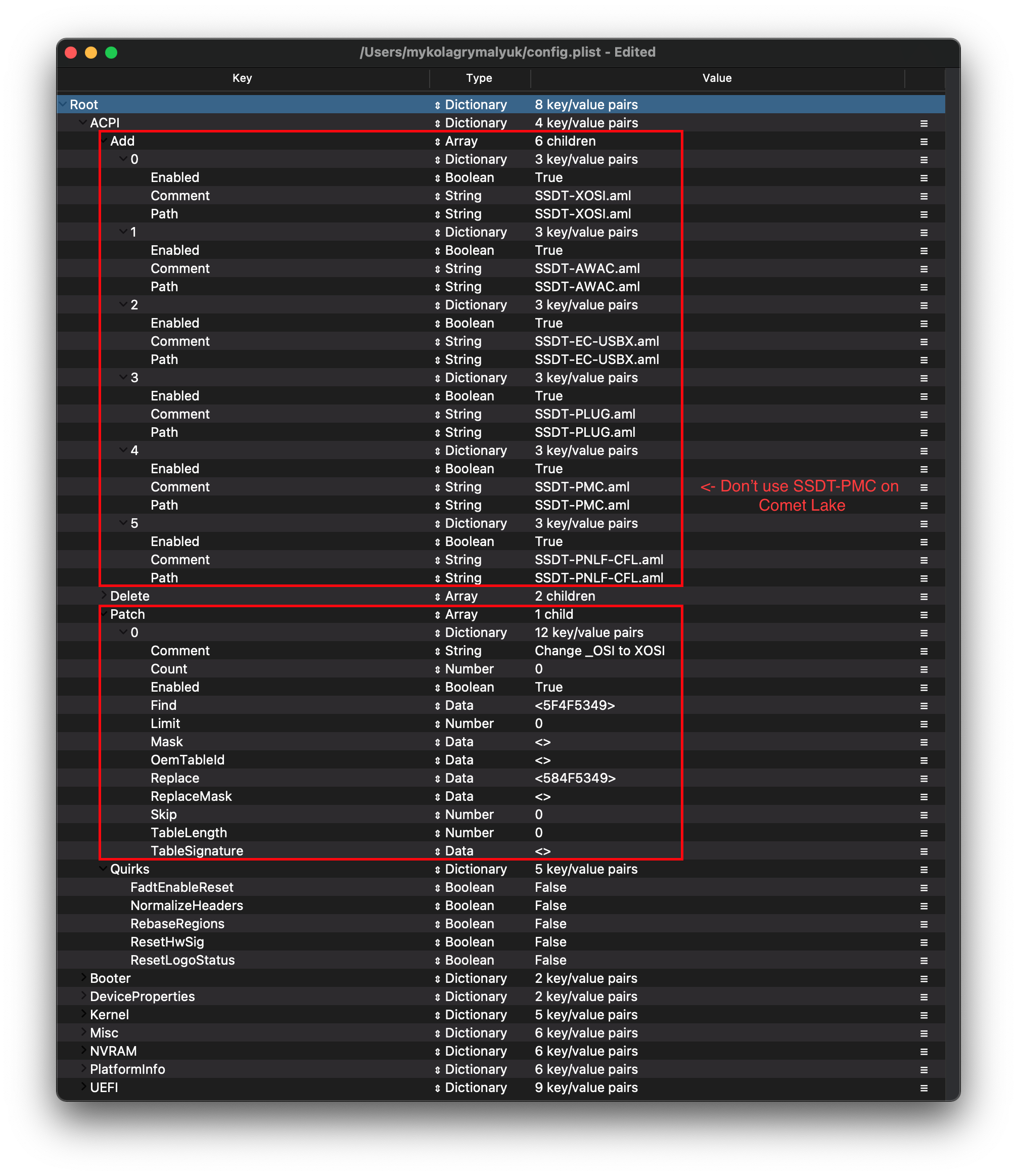
# Add
Info
This is where you'll add SSDTs for your system, these are very important to booting macOS and have many uses like USB maps, disabling unsupported GPUs and such. And with our system, it's even required to boot. Guide on making them found here: Getting started with ACPI
For us we'll need a couple of SSDTs to bring back functionality that Clover provided:
| Required_SSDTs | Description |
|---|---|
| SSDT-PLUG | Allows for native CPU power management on Haswell and newer, see Getting Started With ACPI Guide for more details. |
| SSDT-EC-USBX | Fixes both the embedded controller and USB power, see Getting Started With ACPI Guide for more details. |
| SSDT-GPIO | Creates a stub so VoodooI2C can connect, for those having troubles getting VoodooI2C working can try SSDT-XOSI instead. Note that Intel NUCs do not need this |
| SSDT-PNLF-CFL | Fixes brightness control, see Getting Started With ACPI Guide for more details. Note that Intel NUCs do not need this |
| SSDT-AWAC | This is the 300 series RTC patch, required for most B360, B365, H310, H370, Z390 and some Z370 boards which prevent systems from booting macOS. The alternative is SSDT-RTC0 for when AWAC SSDT is incompatible due to missing the Legacy RTC clock, to check whether you need it and which to use please see Getting started with ACPI page. |
| SSDT-PMC | So true 300 series motherboards(non-Z370) don't declare the FW chip as MMIO in ACPI and so XNU ignores the MMIO region declared by the UEFI memory map. This SSDT brings back NVRAM support. Note that 10th gen CPUs do not need this. See Getting Started With ACPI Guide for more details. |
Note that you should not add your generated DSDT.aml here, it is already in your firmware. So if present, remove the entry for it in your config.plist and under EFI/OC/ACPI.
For those wanting a deeper dive into dumping your DSDT, how to make these SSDTs, and compiling them, please see the Getting started with ACPI page. Compiled SSDTs have a .aml extension(Assembled) and will go into the EFI/OC/ACPI folder and must be specified in your config under ACPI -> Add as well.
# Delete
This blocks certain ACPI tables from loading, for us we can ignore this.
# Patch
Info
This section allows us to dynamically modify parts of the ACPI (DSDT, SSDT, etc.) via OpenCore. For us, we'll need the following:
- OSI rename
- This is required when using SSDT-XOSI as we redirect all OSI calls to this SSDT, this is not needed if you're using SSDT-GPIO
| Comment | String | Change _OSI to XOSI |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | Boolean | YES |
| Count | Number | 0 |
| Limit | Number | 0 |
| Find | Data | 5f4f5349 |
| Replace | Data | 584f5349 |
# Quirks
Settings relating to ACPI, leave everything here as default as we have no use for these quirks.
# Booter
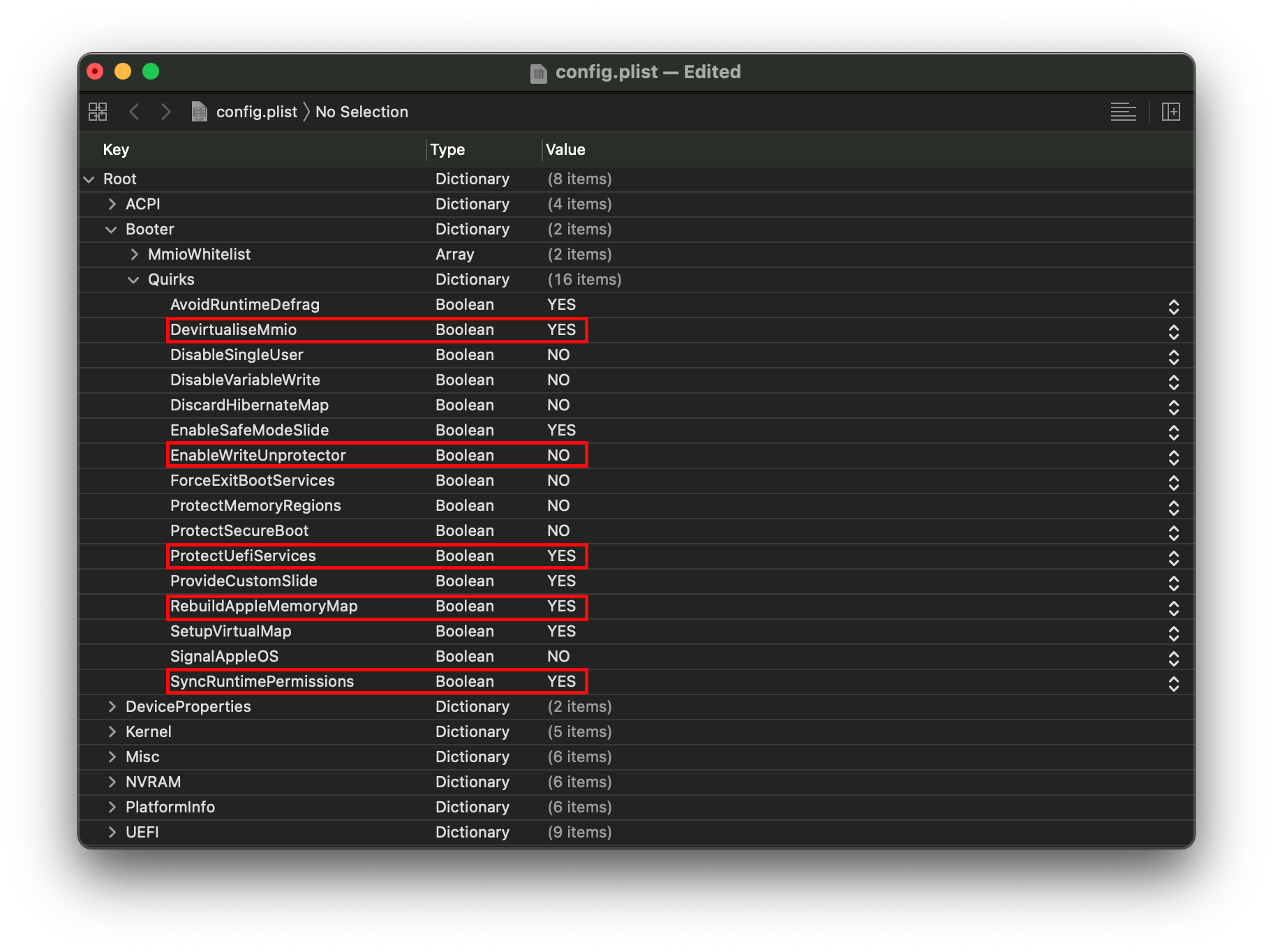
This section is dedicated to quirks relating to boot.efi patching with OpenRuntime, the replacement for AptioMemoryFix.efi
# MmioWhitelist
This section is allowing devices to be pass-through to macOS that are generally ignored, for us we can ignore this section.
# Quirks
Info
Settings relating to boot.efi patching and firmware fixes, for us, we need to change the following:
| Quirk | Enabled |
|---|---|
| DevirtualiseMmio | YES |
| EnableWriteUnprotector | NO |
| ProtectUefiServices | YES |
| RebuildAppleMemoryMap | YES |
| SyncRuntimePermissions | YES |
More in-depth Info
- AvoidRuntimeDefrag: YES
- Fixes UEFI runtime services like date, time, NVRAM, power control, etc
- DevirtualiseMmio: YES
- Reduces Stolen Memory Footprint, expands options for
slide=Nvalues and very helpful with fixing Memory Allocation issues on Z390. RequiresProtectUefiServicesas well on IceLake and Z390 Coffee Lake
- Reduces Stolen Memory Footprint, expands options for
- EnableWriteUnprotector: NO
- This quirk and RebuildAppleMemoryMap can commonly conflict, recommended to enable the latter on newer platforms and disable this entry.
- However, due to issues with OEMs not using the latest EDKII builds you may find that the above combo will result in early boot failures. This is due to missing the
MEMORY_ATTRIBUTE_TABLEand such we recommend disabling RebuildAppleMemoryMap and enabling EnableWriteUnprotector. More info on this is covered in the troubleshooting section
- ProtectUefiServices: YES
- Protects UEFI services from being overridden by the firmware, mainly relevant for VMs, Icelake and Z390 systems'
- If on Z390, enable this quirk
- RebuildAppleMemoryMap: YES
- Generates Memory Map compatible with macOS, can break on some laptop OEM firmwares so if you receive early boot failures disable this
- SetupVirtualMap: YES
- Fixes SetVirtualAddresses calls to virtual addresses, shouldn't be needed on Skylake and newer. Some firmware like Gigabyte may still require it, and will kernel panic without this
- SyncRuntimePermissions: YES
- Fixes alignment with MAT tables and required to boot Windows and Linux with MAT tables, also recommended for macOS. Mainly relevant for RebuildAppleMemoryMap users
# DeviceProperties
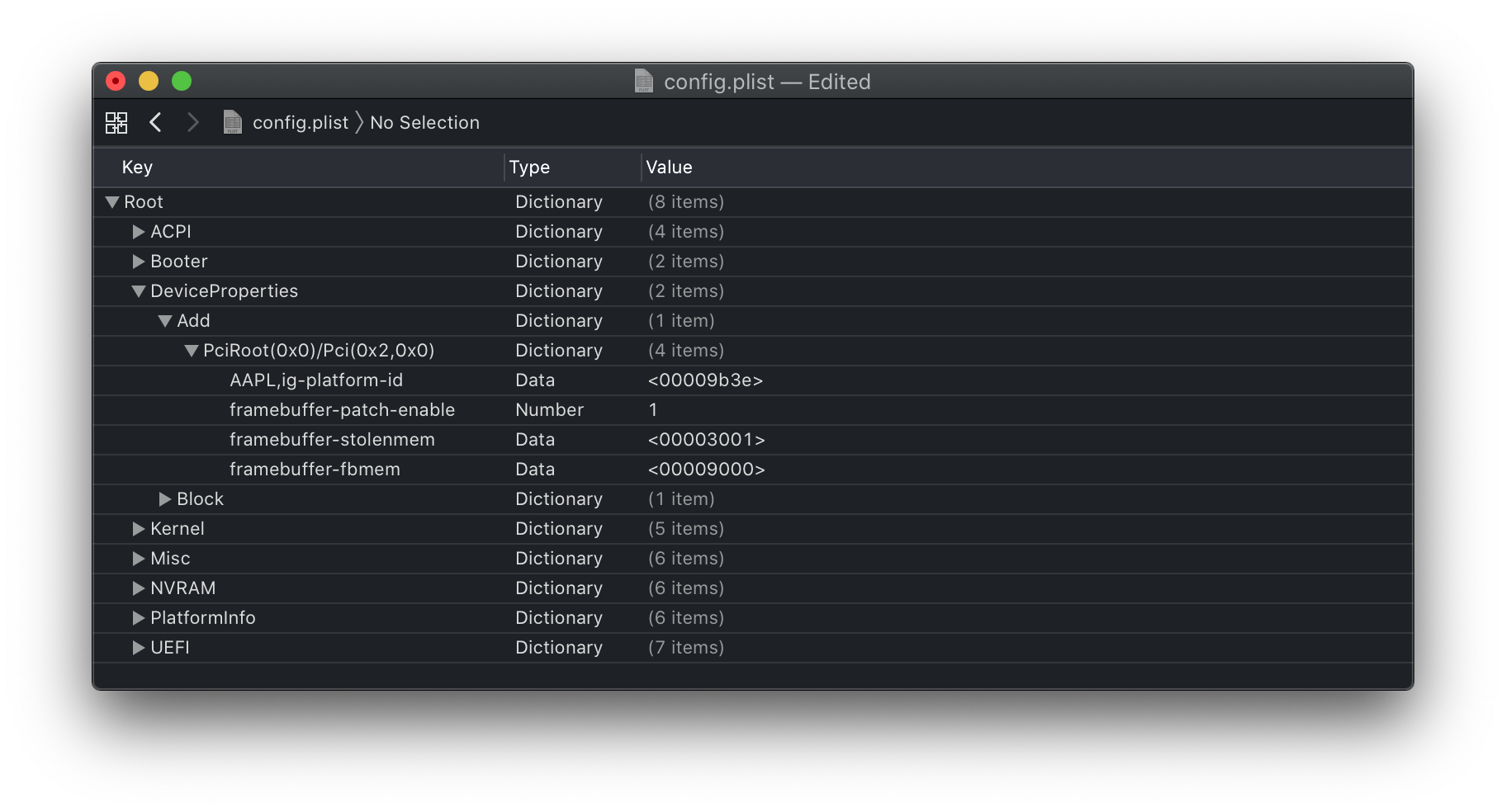
# Add
Sets device properties from a map.
PciRoot(0x0)/Pci(0x2,0x0)
This section is set up via WhateverGreen's Framebuffer Patching Guide and is used for setting important iGPU properties.
When setting up your iGPU, the table below should help with finding the right values to set. Here is an explanation of some values:
- AAPL,ig-platform-id
- This is used internally for setting up the iGPU
- Type
- Whether the entry is recommended for laptops(ie. with built-in displays) or for Intel NUCs(ie. stand alone boxes)
Generally follow these steps when setting up your iGPU properties. Follow the configuration notes below the table if they say anything different:
- When initially setting up your config.plist, only set AAPL,ig-platform-id - this is normally enough
- If you boot and you get no graphics acceleration (7MB VRAM and solid background for dock), then you likely need to try different
AAPL,ig-platform-idvalues, add stolenmem patches, or even add adevice-idproperty.
| AAPL,ig-platform-id | Type | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| 0900A53E | Laptop | Recommended value for UHD630 |
| 00009B3E | Laptop | Recommended value for UHD620 |
| 07009B3E | NUC | Recommended value for UHD 620/630 |
| 0000A53E | NUC | Recommended value for UHD 655 |
# Configuration Notes
- For
UHD630you likely do not need to fake thedevice-idas it is already0x3E9B. If it's anything else, you may usedevice-id=9B3E0000:- You can check under Device Manager in Windows by bring up the iGPU, opening properties, selecting details, and clicking Hardware IDs.
| Key | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| device-id | Data | 9B3E0000 |
- An
UHD620in a Comet Lake CPU requiresdevice-id=9B3E0000:
| Key | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| device-id | Data | 9B3E0000 |
- In some cases where you cannot set the DVMT-prealloc of these cards to 64MB higher in your UEFI Setup, you may get a kernel panic. Usually they're configured for 32MB of DVMT-prealloc, in that case these values are added to your iGPU Properties
| Key | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| framebuffer-patch-enable | Data | 01000000 |
| framebuffer-stolenmem | Data | 00003001 |
| framebuffer-fbmem | Data | 00009000 |
PciRoot(0x0)/Pci(0x1b,0x0)
layout-id
- Applies AppleALC audio injection, you'll need to do your own research on which codec your motherboard has and match it with AppleALC's layout. AppleALC Supported Codecs.
- You can delete this property outright as it's unused for us at this time
For us, we'll be using the boot argument alcid=xxx instead to accomplish this. alcid will override all other layout-IDs present. More info on this is covered in the Post-Install Page
# Delete
Removes device properties from the map, for us we can ignore this
# Kernel
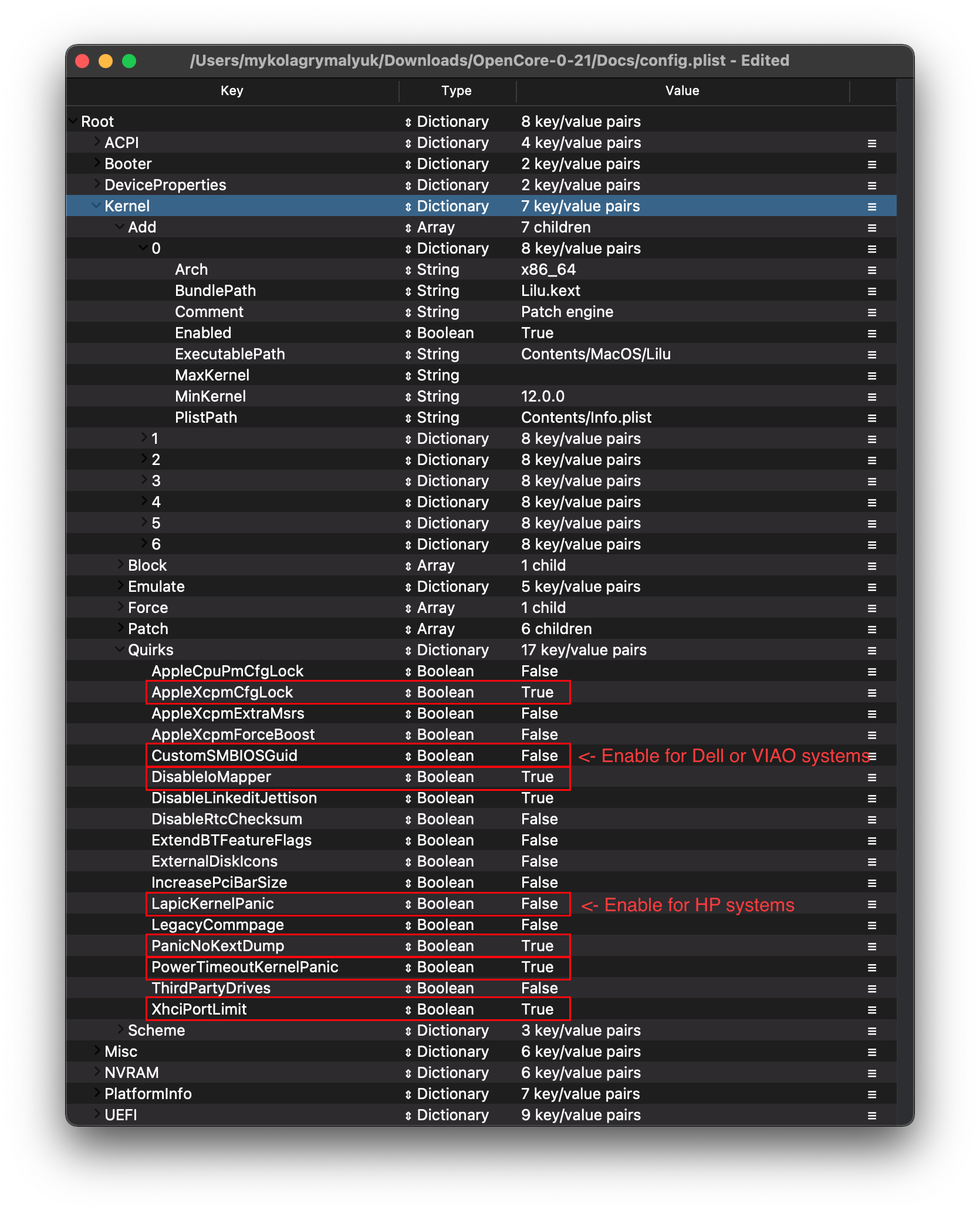
# Add
Here's where we specify which kexts to load, in what specific order to load, and what architectures each kext is meant for. By default we recommend leaving what ProperTree has done, however for 32-bit CPUs please see below:
More in-depth Info
The main thing you need to keep in mind is:
- Load order
- Remember that any plugins should load after its dependencies
- This means kexts like Lilu must come before VirtualSMC, AppleALC, WhateverGreen, etc
A reminder that ProperTree users can run Cmd/Ctrl + Shift + R to add all their kexts in the correct order without manually typing each kext out.
- Arch
- Architectures supported by this kext
- Currently supported values are
Any,i386(32-bit), andx86_64(64-bit)
- BundlePath
- Name of the kext
- ex:
Lilu.kext
- Enabled
- Self-explanatory, either enables or disables the kext
- ExecutablePath
- Path to the actual executable is hidden within the kext, you can see what path your kext has by right-clicking and selecting
Show Package Contents. Generally, they'll beContents/MacOS/Kextbut some have kexts hidden within underPluginfolder. Do note that plist only kexts do not need this filled in. - ex:
Contents/MacOS/Lilu
- Path to the actual executable is hidden within the kext, you can see what path your kext has by right-clicking and selecting
- MinKernel
- Lowest kernel version your kext will be injected into, see below table for possible values
- ex.
12.00.00for OS X 10.8
- MaxKernel
- Highest kernel version your kext will be injected into, see below table for possible values
- ex.
11.99.99for OS X 10.7
- PlistPath
- Path to the
info.plisthidden within the kext - ex:
Contents/Info.plist
- Path to the
Kernel Support Table
| OS X Version | MinKernel | MaxKernel |
|---|---|---|
| 10.4 | 8.0.0 | 8.99.99 |
| 10.5 | 9.0.0 | 9.99.99 |
| 10.6 | 10.0.0 | 10.99.99 |
| 10.7 | 11.0.0 | 11.99.99 |
| 10.8 | 12.0.0 | 12.99.99 |
| 10.9 | 13.0.0 | 13.99.99 |
| 10.10 | 14.0.0 | 14.99.99 |
| 10.11 | 15.0.0 | 15.99.99 |
| 10.12 | 16.0.0 | 16.99.99 |
| 10.13 | 17.0.0 | 17.99.99 |
| 10.14 | 18.0.0 | 18.99.99 |
| 10.15 | 19.0.0 | 19.99.99 |
| 11 | 20.0.0 | 20.99.99 |
# Emulate
Needed for spoofing unsupported CPUs like Pentiums and Celerons
- CpuidMask: Leave this blank
- CpuidData: Leave this blank
# Force
Used for loading kexts off system volume, only relevant for older operating systems where certain kexts are not present in the cache(ie. IONetworkingFamily in 10.6).
For us, we can ignore.
# Block
Blocks certain kexts from loading. Not relevant for us.
# Patch
Patches both the kernel and kexts.
# Quirks
Info
Settings relating to the kernel, for us we'll be enabling the following:
| Quirk | Enabled | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| AppleXcpmCfgLock | YES | Not needed if CFG-Lock is disabled in the BIOS |
| DisableIOMapper | YES | Not needed if VT-D is disabled in the BIOS |
| LapicKernelPanic | NO | HP Machines will require this quirk |
| PanicNoKextDump | YES | |
| PowerTimeoutKernelPanic | YES | |
| XhciPortLimit | YES |
More in-depth Info
- AppleCpuPmCfgLock: NO
- Only needed when CFG-Lock can't be disabled in BIOS
- Only applicable for Ivy Bridge and older
- Note: Broadwell and older require this when running 10.10 or older
- AppleXcpmCfgLock: YES
- Only needed when CFG-Lock can't be disabled in BIOS
- Only applicable for Haswell and newer
- Note: Ivy Bridge-E is also included as it's XCPM capable
- CustomSMBIOSGuid: NO
- Performs GUID patching for UpdateSMBIOSMode set to
Custom. Usually relevant for Dell laptops - Enabling this quirk with UpdateSMBIOSMode Custom mode can also disable SMBIOS injection into "non-Apple" OSes however we do not endorse this method as it breaks Bootcamp compatibility. Use at your own risk
- Performs GUID patching for UpdateSMBIOSMode set to
- DisableIoMapper: YES
- Needed to get around VT-D if either unable to disable in BIOS or needed for other operating systems, much better alternative to
dart=0as SIP can stay on in Catalina
- Needed to get around VT-D if either unable to disable in BIOS or needed for other operating systems, much better alternative to
- DisableLinkeditJettison: YES
- Allows Lilu and others to have more reliable performance without
keepsyms=1
- Allows Lilu and others to have more reliable performance without
- DisableRtcChecksum: NO
- Prevents AppleRTC from writing to primary checksum (0x58-0x59), required for users who either receive BIOS reset or are sent into Safe mode after reboot/shutdown
- ExtendBTFeatureFlags NO
- Helpful for those having continuity issues with non-Apple/non-Fenvi cards
- LapicKernelPanic: NO
- Disables kernel panic on AP core lapic interrupt, generally needed for HP systems. Clover equivalent is
Kernel LAPIC
- Disables kernel panic on AP core lapic interrupt, generally needed for HP systems. Clover equivalent is
- LegacyCommpage: NO
- Resolves SSSE3 requirement for 64 Bit CPUs in macOS, mainly relevant for 64-Bit Pentium 4 CPUs(ie. Prescott)
- PanicNoKextDump: YES
- Allows for reading kernel panics logs when kernel panics occur
- PowerTimeoutKernelPanic: YES
- Helps fix kernel panics relating to power changes with Apple drivers in macOS Catalina, most notably with digital audio.
- XhciPortLimit: YES
- This is actually the 15 port limit patch, don't rely on it as it's not a guaranteed solution for fixing USB. Please create a USB map when possible.
The reason being is that UsbInjectAll reimplements builtin macOS functionality without proper current tuning. It is much cleaner to just describe your ports in a single plist-only kext, which will not waste runtime memory and such
# Scheme
Settings related to legacy booting(ie. 10.4-10.6), for majority you can skip however for those planning to boot legacy OSes you can see below:
More in-depth Info
FuzzyMatch: True
- Used for ignoring checksums with kernelcache, instead opting for the latest cache available. Can help improve boot performance on many machines in 10.6
KernelArch: x86_64
- Set the kernel's arch type, you can choose between
Auto,i386(32-bit), andx86_64(64-bit). - If you're booting older OSes which require a 32-bit kernel(ie. 10.4 and 10.5) we recommend to set this to
Autoand let macOS decide based on your SMBIOS. See below table for supported values:- 10.4-10.5 —
x86_64,i386ori386-user32i386-user32refers 32-bit userspace, so 32-bit CPUs must use this(or CPUs missing SSSE3)x86_64will still have a 32-bit kernelspace however will ensure 64-bit userspace in 10.4/5
- 10.6 —
i386,i386-user32, orx86_64 - 10.7 —
i386orx86_64 - 10.8 or newer —
x86_64
- 10.4-10.5 —
- Set the kernel's arch type, you can choose between
KernelCache: Auto
- Set kernel cache type, mainly useful for debugging and so we recommend
Autofor best support
- Set kernel cache type, mainly useful for debugging and so we recommend
# Misc
# Boot
Settings for boot screen (Leave everything as default).
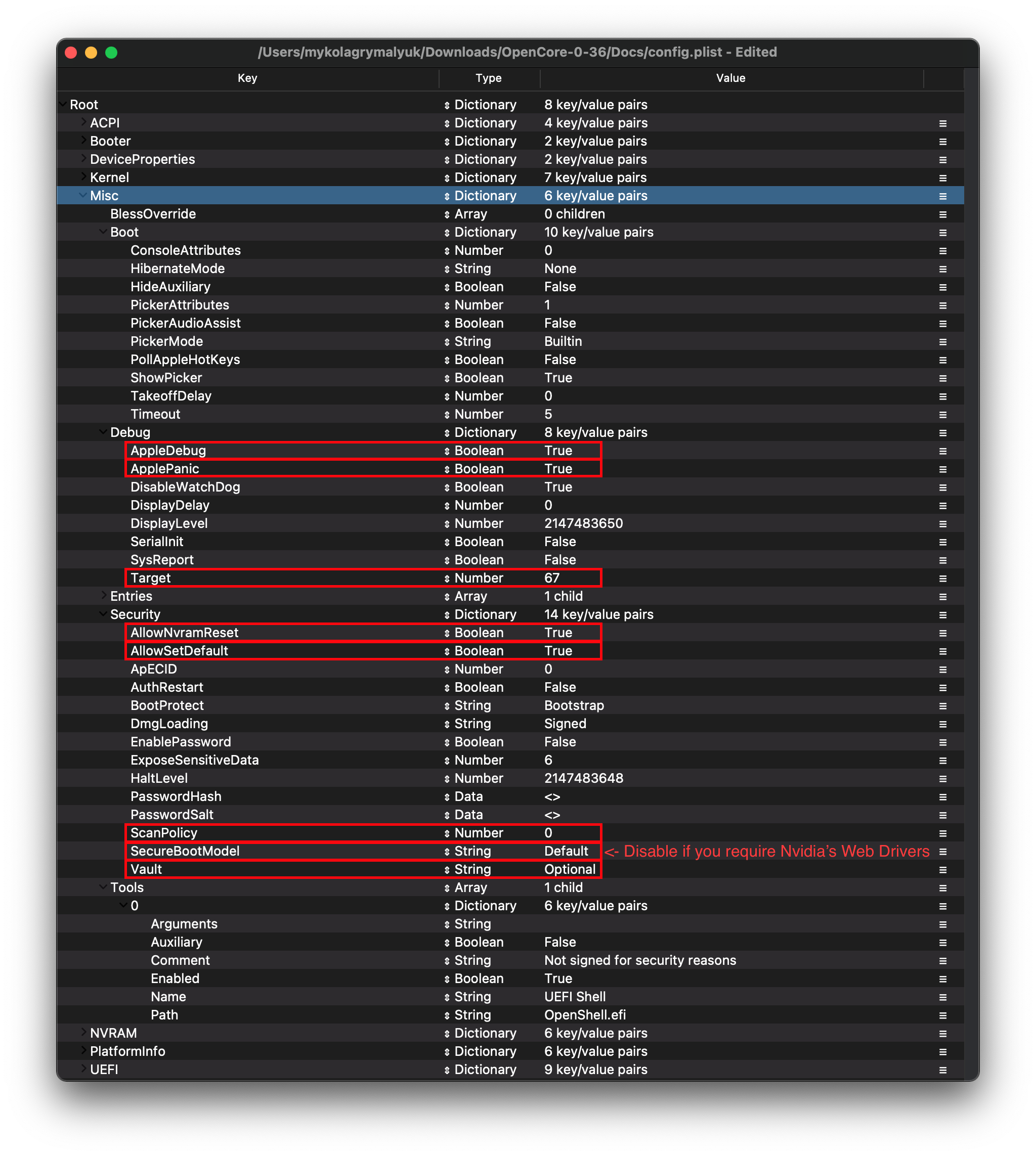
# Debug
Info
Helpful for debugging OpenCore boot issues(We'll be changing everything but DisplayDelay):
| Quirk | Enabled |
|---|---|
| AppleDebug | YES |
| ApplePanic | YES |
| DisableWatchDog | YES |
| Target | 67 |
More in-depth Info
- AppleDebug: YES
- Enables boot.efi logging, useful for debugging. Note this is only supported on 10.15.4 and newer
- ApplePanic: YES
- Attempts to log kernel panics to disk
- DisableWatchDog: YES
- Disables the UEFI watchdog, can help with early boot issues
- DisplayLevel:
2147483650- Shows even more debug information, requires debug version of OpenCore
- SerialInit: NO
- Needed for setting up serial output with OpenCore
- SysReport: NO
- Helpful for debugging such as dumping ACPI tables
- Note that this is limited to DEBUG versions of OpenCore
- Target:
67- Shows more debug information, requires debug version of OpenCore
These values are based of those calculated in OpenCore debugging
# Security
Info
Security is pretty self-explanatory, do not skip. We'll be changing the following:
| Quirk | Enabled | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| AllowNvramReset | YES | |
| AllowSetDefault | YES | |
| BlacklistAppleUpdate | YES | |
| ScanPolicy | 0 | |
| SecureBootModel | Default | This is a word and is case-sensitive, set to Disabled if you do not want secure boot(ie. you require Nvidia's Web Drivers) |
| Vault | Optional | This is a word, it is not optional to omit this setting. You will regret it if you don't set it to Optional, note that it is case-sensitive |
More in-depth Info
- AllowNvramReset: YES
- Allows for NVRAM reset both in the boot picker and when pressing
Cmd+Opt+P+R
- Allows for NVRAM reset both in the boot picker and when pressing
- AllowSetDefault: YES
- Allow
CTRL+EnterandCTRL+Indexto set default boot device in the picker
- Allow
- ApECID: 0
- Used for netting personalized secure-boot identifiers, currently this quirk is unreliable due to a bug in the macOS installer so we highly encourage you to leave this as default.
- AuthRestart: NO
- Enables Authenticated restart for FileVault 2 so password is not required on reboot. Can be considered a security risk so optional
- BlacklistAppleUpdate: YES
- Used for blocking firmware updates, used as extra level of protection as macOS Big Sur no longer uses
run-efi-updatervariable
- Used for blocking firmware updates, used as extra level of protection as macOS Big Sur no longer uses
- BootProtect: None
- Allows the use of Bootstrap.efi inside EFI/OC/Bootstrap instead of BOOTx64.efi, useful for those wanting to either boot with rEFInd or avoid BOOTx64.efi overwrites from Windows. Proper use of this quirks is covered here: Using Bootstrap.efi
- DmgLoading: Signed
- Ensures only signed DMGs load
- ExposeSensitiveData:
6- Shows more debug information, requires debug version of OpenCore
- Vault:
Optional- We won't be dealing vaulting so we can ignore, you won't boot with this set to Secure
- This is a word, it is not optional to omit this setting. You will regret it if you don't set it to
Optional, note that it is case-sensitive
- ScanPolicy:
00allows you to see all drives available, please refer to Security section for further details. Will not boot USB devices with this set to default
- SecureBootModel: Default
- Enables Apple's secure boot functionality in macOS, please refer to Security section for further details.
- Note: Users may find upgrading OpenCore on an already installed system can result in early boot failures. To resolve this, see here: Stuck on OCB: LoadImage failed - Security Violation
# Tools
Used for running OC debugging tools like the shell, ProperTree's snapshot function will add these for you.
# Entries
Used for specifying irregular boot paths that can't be found naturally with OpenCore.
Won't be covered here, see 8.6 of Configuration.pdf for more info
# NVRAM
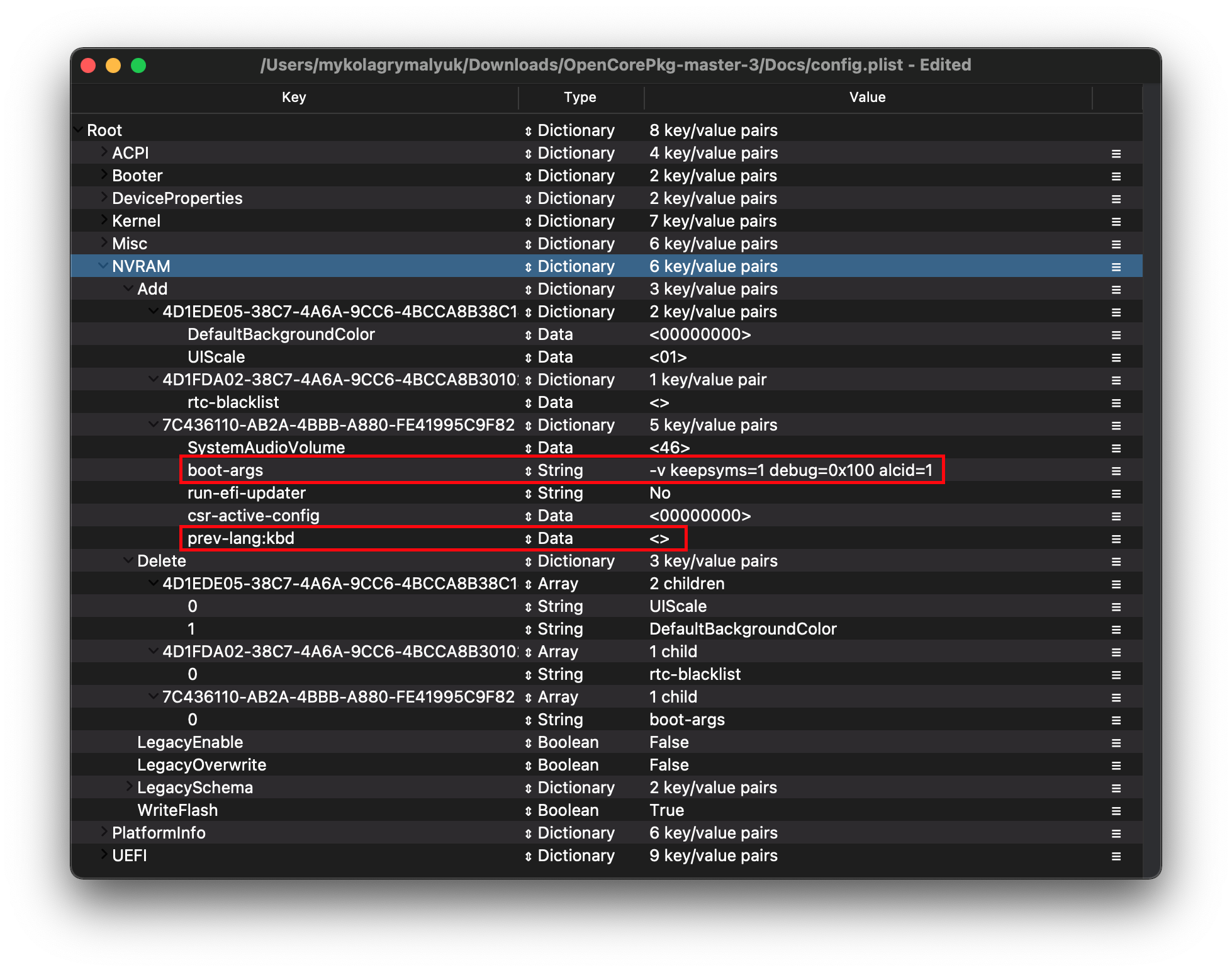
# Add
4D1EDE05-38C7-4A6A-9CC6-4BCCA8B38C14
Used for OpenCore's UI scaling, default will work for us. See in-depth section for more info
More in-depth Info
Booter Path, mainly used for UI Scaling
UIScale:
01: Standard resolution02: HiDPI (generally required for FileVault to function correctly on smaller displays)
DefaultBackgroundColor: Background color used by boot.efi
00000000: Syrah BlackBFBFBF00: Light Gray
4D1FDA02-38C7-4A6A-9CC6-4BCCA8B30102
OpenCore's NVRAM GUID, mainly relevant for RTCMemoryFixup users
More in-depth Info
- rtc-blacklist: <>
- To be used in conjunction with RTCMemoryFixup, see here for more info: Fixing RTC write issues
- Most users can ignore this section
7C436110-AB2A-4BBB-A880-FE41995C9F82
System Integrity Protection bitmask
- General Purpose boot-args:
| boot-args | Description |
|---|---|
| -v | This enables verbose mode, which shows all the behind-the-scenes text that scrolls by as you're booting instead of the Apple logo and progress bar. It's invaluable to any Hackintosher, as it gives you an inside look at the boot process, and can help you identify issues, problem kexts, etc. |
| debug=0x100 | This disables macOS's watchdog which helps prevents a reboot on a kernel panic. That way you can hopefully glean some useful info and follow the breadcrumbs to get past the issues. |
| keepsyms=1 | This is a companion setting to debug=0x100 that tells the OS to also print the symbols on a kernel panic. That can give some more helpful insight as to what's causing the panic itself. |
| alcid=1 | Used for setting layout-id for AppleALC, see supported codecs to figure out which layout to use for your specific system. More info on this is covered in the Post-Install Page |
- GPU-Specific boot-args:
| boot-args | Description |
|---|---|
| -wegnoegpu | Used for disabling all other GPUs than the integrated Intel iGPU, useful for those wanting to run newer versions of macOS where their dGPU isn't supported |
csr-active-config:
00000000- Settings for 'System Integrity Protection' (SIP). It is generally recommended to change this with
csrutilvia the recovery partition. - csr-active-config by default is set to
00000000which enables System Integrity Protection. You can choose a number of different values but overall we recommend keeping this enabled for best security practices. More info can be found in our troubleshooting page: Disabling SIP
- Settings for 'System Integrity Protection' (SIP). It is generally recommended to change this with
run-efi-updater:
No- This is used to prevent Apple's firmware update packages from installing and breaking boot order; this is important as these firmware updates (meant for Macs) will not work.
prev-lang:kbd: <>
- Needed for non-latin keyboards in the format of
lang-COUNTRY:keyboard, recommended to keep blank though you can specify it(Default in Sample config is Russian): - American:
en-US:0(656e2d55533a30in HEX) - Full list can be found in AppleKeyboardLayouts.txt
- Hint:
prev-lang:kbdcan be changed into a String so you can inputen-US:0directly instead of converting to HEX
- Needed for non-latin keyboards in the format of
| Key | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| prev-lang:kbd | String | en-US:0 |
# Delete
Forcibly rewrites NVRAM variables, do note that Add will not overwrite values already present in NVRAM so values like boot-args should be left alone.
LegacyEnable: NO
- Allows for NVRAM to be stored on nvram.plist, needed for systems without native NVRAM
LegacyOverwrite: NO
- Permits overwriting firmware variables from nvram.plist, only needed for systems without native NVRAM
LegacySchema
- Used for assigning NVRAM variables, used with LegacyEnable set to YES
WriteFlash: YES
- Enables writing to flash memory for all added variables.
# PlatformInfo
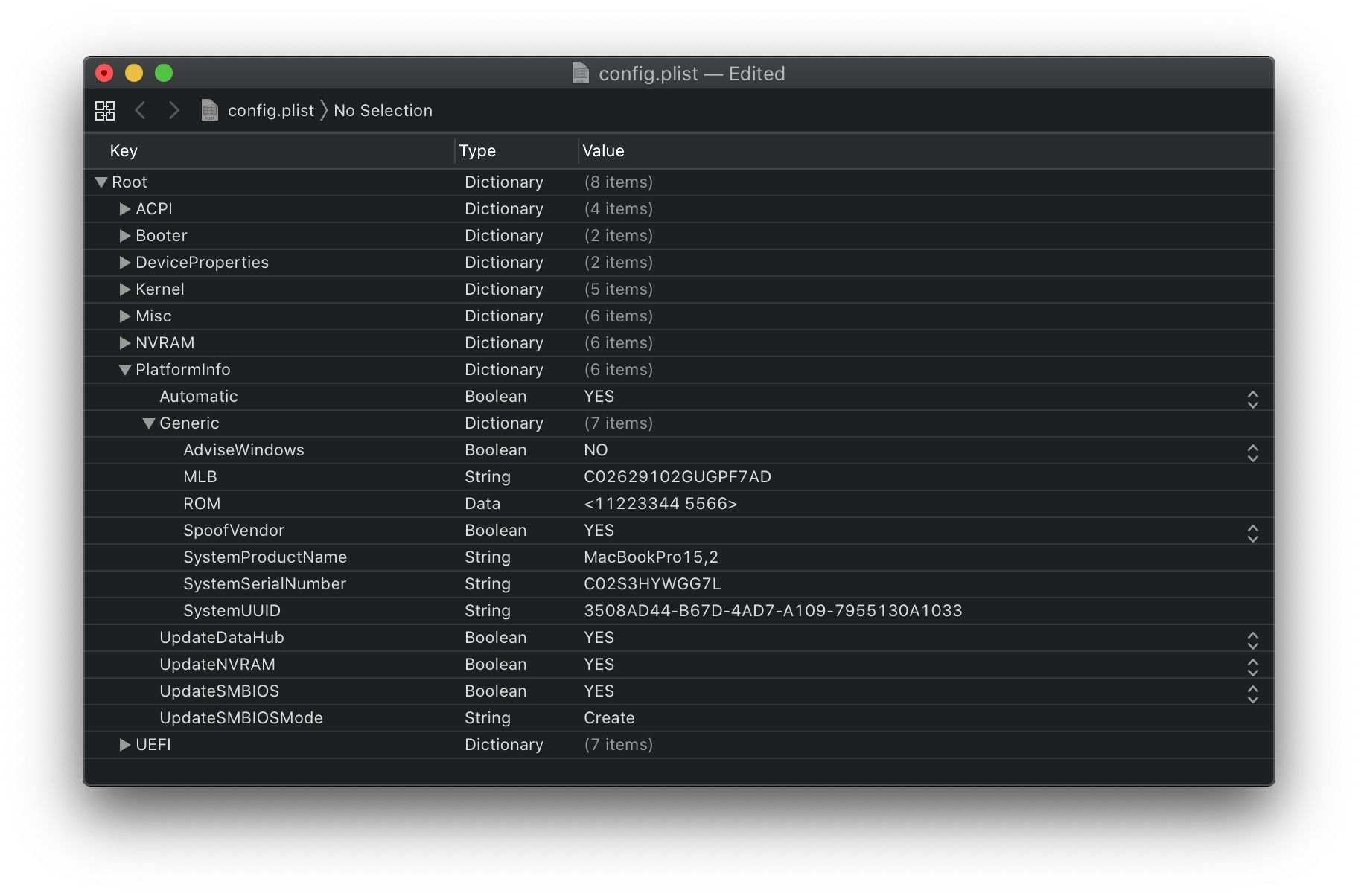
Info
For setting up the SMBIOS info, we'll use CorpNewt's GenSMBIOS application.
For this Coffee Lake Plus example, we'll chose the MacBookPro16,1 SMBIOS - this is done intentionally for compatibility's sake. The breakdown is as follows(note that the below SMBIOS require macOS 10.15, Catalina):
| SMBIOS | CPU Type | GPU Type | Display Size | Touch ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MacBookPro16,1 | Hexa/Octa Core 45w | iGPU: UHD 630 + dGPU: 5300/5500M | 15" | Yes |
| MacBookPro16,3 | Quad Core 15w | iGPU: Iris 645 | 13" | Yes |
| MacBookPro16,4 | Hexa/Octa Core 45w | iGPU: UHD 630 + dGPU: 5600M | 15" | Yes |
| Macmini8,1 | NUC Systems | HD 6000/Iris Pro 6200 | N/A | No |
Run GenSMBIOS, pick option 1 for downloading MacSerial and Option 3 for selecting out SMBIOS. This will give us an output similar to the following:
#######################################################
# MacBookPro16,1 SMBIOS Info #
#######################################################
Type: MacBookPro16,1
Serial: C02XG0FDH7JY
Board Serial: C02839303QXH69FJA
SmUUID: DBB364D6-44B2-4A02-B922-AB4396F16DA8
- Note: MacSerial currently does not support Linux, so you must grab a Windows or macOS machine to generate the MacBookPro16,2+ values
The Type part gets copied to Generic -> SystemProductName.
The Serial part gets copied to Generic -> SystemSerialNumber.
The Board Serial part gets copied to Generic -> MLB.
The SmUUID part gets copied to Generic -> SystemUUID.
We set Generic -> ROM to either an Apple ROM (dumped from a real Mac), your NIC MAC address, or any random MAC address (could be just 6 random bytes, for this guide we'll use 11223300 0000. After install follow the Fixing iServices page on how to find your real MAC Address)
Reminder that you want either an invalid serial or valid serial numbers but those not in use, you want to get a message back like: "Invalid Serial" or "Purchase Date not Validated"
Automatic: YES
- Generates PlatformInfo based on Generic section instead of DataHub, NVRAM, and SMBIOS sections
# Generic
More in-depth Info
AdviseWindows: NO
- Used for when the EFI partition isn't first on the Windows drive
SystemMemoryStatus: Auto
- Sets whether memory is soldered or not in SMBIOS info, purely cosmetic and so we recommend
Auto
- Sets whether memory is soldered or not in SMBIOS info, purely cosmetic and so we recommend
ProcessorType:
0- Set to
0for automatic type detection, however this value can be overridden if desired. See AppleSmBios.h for possible values
- Set to
SpoofVendor: YES
- Swaps vendor field for Acidanthera, generally not safe to use Apple as a vendor in most case
UpdateDataHub: YES
- Update Data Hub fields
UpdateNVRAM: YES
- Update NVRAM fields
UpdateSMBIOS: YES
- Updates SMBIOS fields
UpdateSMBIOSMode: Create
- Replace the tables with newly allocated EfiReservedMemoryType, use
Customon Dell laptops requiringCustomSMBIOSGuidquirk - Setting to
CustomwithCustomSMBIOSGuidquirk enabled can also disable SMBIOS injection into "non-Apple" OSes however we do not endorse this method as it breaks Bootcamp compatibility. Use at your own risk
- Replace the tables with newly allocated EfiReservedMemoryType, use
# UEFI
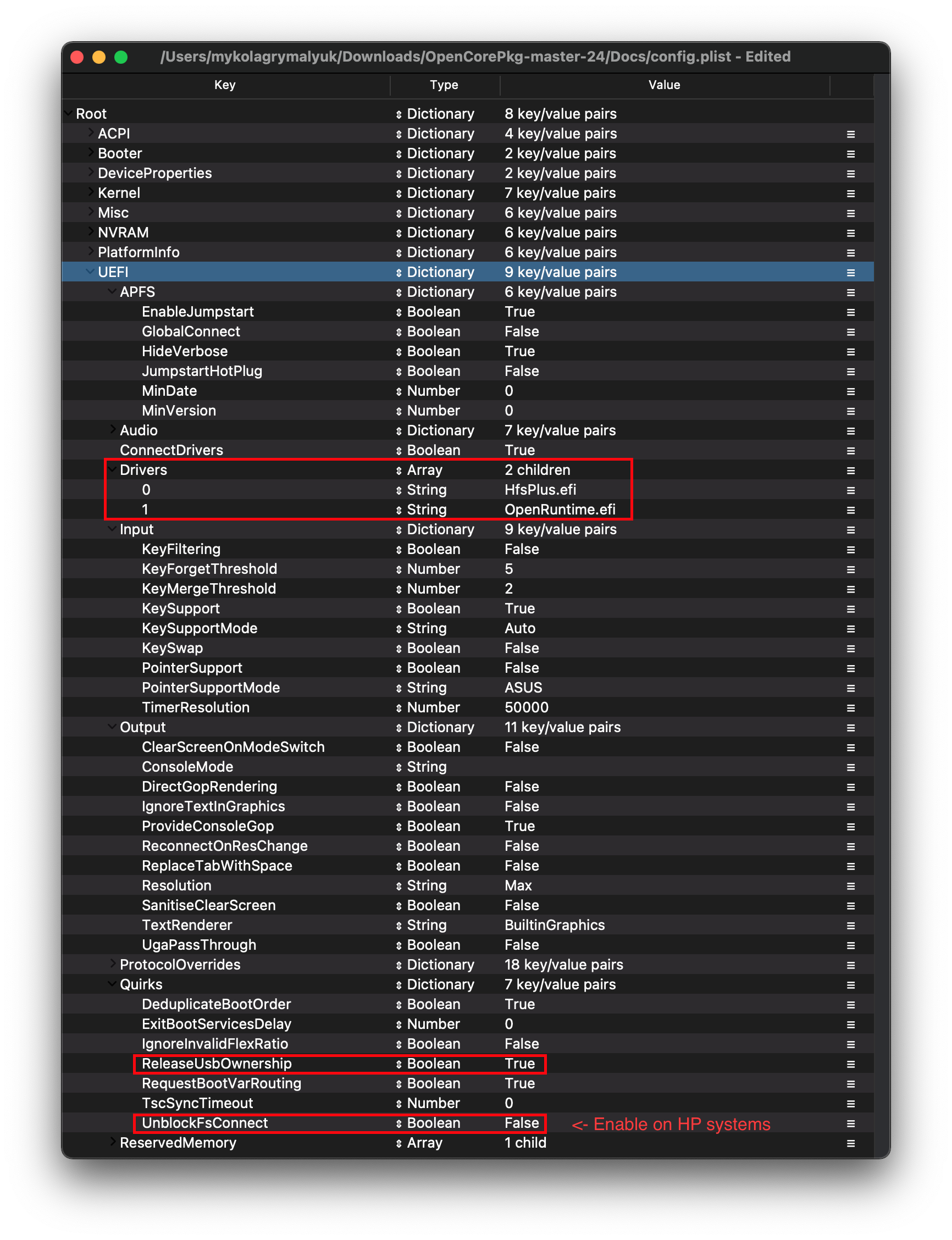
ConnectDrivers: YES
- Forces .efi drivers, change to NO will automatically connect added UEFI drivers. This can make booting slightly faster, but not all drivers connect themselves. E.g. certain file system drivers may not load.
# Drivers
Add your .efi drivers here.
Only drivers present here should be:
- HfsPlus.efi
- OpenRuntime.efi
# APFS
Settings related to the APFS driver, leave everything here as default.
# Audio
Related to AudioDxe settings, for us we'll be ignoring(leave as default). This is unrelated to audio support in macOS.
- For further use of AudioDxe and the Audio section, please see the Post Install page: Add GUI and Boot-chime
# Input
Related to boot.efi keyboard passthrough used for FileVault and Hotkey support, leave everything here as default as we have no use for these quirks. See here for more details: Security and FileVault
# Output
Relating to OpenCore's visual output, leave everything here as default as we have no use for these quirks.
# ProtocolOverrides
Mainly relevant for Virtual machines, legacy macs and FileVault users. See here for more details: Security and FileVault
# Quirks
Info
Relating to quirks with the UEFI environment, for us we'll be changing the following:
| Quirk | Enabled | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| ReleaseUsbOwnership | YES | |
| UnblockFsConnect | NO | Needed mainly by HP motherboards |
More in-depth Info
ReleaseUsbOwnership: YES
- Releases USB controller from firmware driver, needed for when your firmware doesn't support EHCI/XHCI Handoff. Most laptops have garbage firmwares so we'll need this as well
RequestBootVarRouting: YES
- Redirects AptioMemoryFix from
EFI_GLOBAL_VARIABLE_GUIDtoOC_VENDOR_VARIABLE_GUID. Needed for when firmware tries to delete boot entries and is recommended to be enabled on all systems for correct update installation, Startup Disk control panel functioning, etc.
- Redirects AptioMemoryFix from
UnblockFsConnect: NO
- Some firmware block partition handles by opening them in By Driver mode, which results in File System protocols being unable to install. Mainly relevant for HP systems when no drives are listed
# ReservedMemory
Used for exempting certain memory regions from OSes to use, mainly relevant for Sandy Bridge iGPUs or systems with faulty memory. Use of this quirk is not covered in this guide
# Cleaning up
And now you're ready to save and place it into your EFI under EFI/OC.
For those having booting issues, please make sure to read the Troubleshooting section first and if your questions are still unanswered we have plenty of resources at your disposal:
Sanity check:
So thanks to the efforts of Ramus, we also have an amazing tool to help verify your config for those who may have missed something:
Note that this tool is neither made nor maintained by Dortania, any and all issues with this site should be sent here: Sanity Checker Repo
# Config reminders
HP Users:
- Kernel -> Quirks -> LapicKernelPanic -> True
- You will get a kernel panic on LAPIC otherwise
- UEFI -> Quirks -> UnblockFsConnect -> True
Dell Users:
For Skylake and newer:
- Kernel -> Quirk -> CustomSMBIOSGuid -> True
- PlatformInfo -> UpdateSMBIOSMode -> Custom
# Intel BIOS settings
- Note: Most of these options may not be present in your firmware, we recommend matching up as closely as possible but don't be too concerned if many of these options are not available in your BIOS
# Disable
- Fast Boot
- Secure Boot
- Serial/COM Port
- Parallel Port
- VT-d (can be enabled if you set
DisableIoMapperto YES) - CSM
- Thunderbolt(For initial install, as Thunderbolt can cause issues if not setup correctly)
- Intel SGX
- Intel Platform Trust
- CFG Lock (MSR 0xE2 write protection)(This must be off, if you can't find the option then enable
AppleXcpmCfgLockunder Kernel -> Quirks. Your hack will not boot with CFG-Lock enabled)
# Enable
- VT-x
- Above 4G decoding
- Hyper-Threading
- Execute Disable Bit
- EHCI/XHCI Hand-off
- OS type: Windows 8.1/10 UEFI Mode
- DVMT Pre-Allocated(iGPU Memory): 64MB
- SATA Mode: AHCI
